Have you ever wondered about the fascinating traits of banana spiders? These venomous arachnids possess unique characteristics that make them both intriguing and captivating.
From their impressive size and intricate webs to their ability to change the color of their surroundings, banana spiders are truly remarkable creatures.
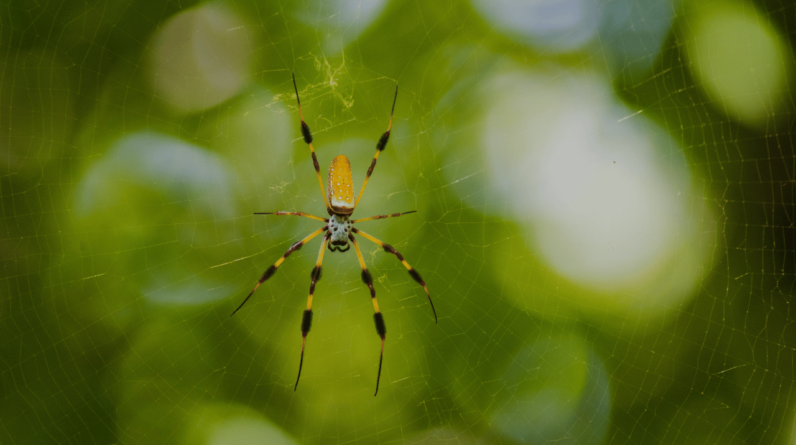
With a body length ranging from 1 to 3 inches, the female banana spider is larger than the male and boasts a stunning spotted orange, yellow, or tan abdomen.
Their webs, which can reach an impressive diameter of 6 feet or more, are meticulously constructed and often match the colors of their environment.
Banana spiders are primarily found in warm regions with high humidity, such as heavily forested or swampy areas, as well as urban areas with abundant food and artificial light.
Their diet consists of flying or jumping insects, which they capture and subdue with their venomous bite.
While banana spiders are not typically dangerous to humans, it is important to note that individuals with pre-existing conditions may be more susceptible to their venom.
In this article, we will explore the intriguing world of banana spiders, delving into their diet, habitat, behavior, and potential dangers.
Get ready to uncover the secrets of these fascinating arachnids and gain a mastery of their captivating traits.
What They Eat
Banana spiders, like we mentioned earlier, primarily feed on flying or jumping insects. Their hunting techniques are fascinating and precise. These venomous arachnids carefully select their prey, using their keen eyesight and vibration-sensing leg hairs to detect movement.
Once a potential meal is spotted, the banana spider quickly immobilizes it using its venomous bite. But their hunting prowess doesn’t stop there. Banana spiders also utilize their silk production skills to construct large, intricate webs. These webs can reach impressive sizes, often exceeding 6 feet in diameter.
The silk is not only used to trap their food but also to communicate with potential mates. It’s truly remarkable how these arachnids have evolved to be such efficient predators, relying on their venom and silk to sustain themselves in their warm, humid habitats.
Habitat and Behavior of Banana Spiders
Explore the captivating habitat and behavior of these intriguing creatures, as they thrive in warm, humid regions and demonstrate fascinating adaptations.
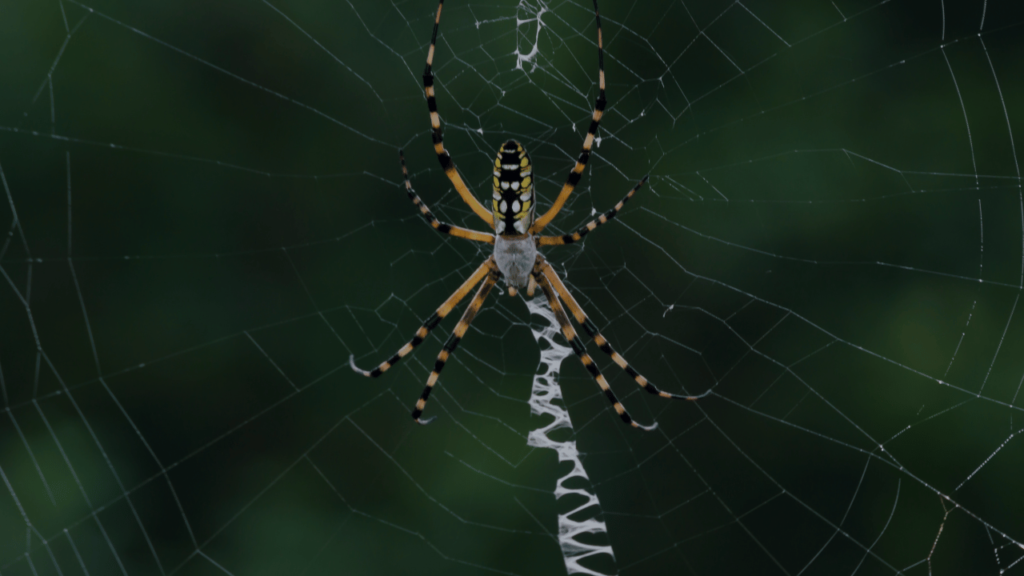
Banana spiders are known for their impressive web construction skills. The female banana spider builds large, intricate webs that can reach up to 6 feet or more in diameter. These webs are designed to trap their prey, primarily flying or jumping insects. What’s even more fascinating is that banana spiders can change the color of their webs to match their surroundings, making them even more effective at catching prey.
When it comes to mating, banana spiders have unique rituals. The male banana spider will approach the female’s web and gently tap it to announce his presence. If the female is receptive, she will respond by tapping back. This interaction continues until the male is allowed to approach and mate with the female.
It’s important to note that banana spiders are not aggressive and typically only bite when provoked. So, while their habitat and behavior may be intriguing, there is no need to fear these venomous arachnids.
Potential Dangers of Banana Spiders
Watch out for the potential dangers associated with these creatures, as their bites can cause mild discomfort similar to a bee sting. While banana spiders aren’t typically dangerous to humans, individuals with pre-existing conditions should exercise caution.
It’s important to note that their venomous bites can result in slight swelling or blistering. However, when comparing banana spiders to other venomous spiders, such as the Sydney funnel web spider, their venom is considered less potent. The Sydney funnel web spider, found in Australia, possesses fangs strong enough to pierce leather and its bite causes immediate pain and other symptoms.
In contrast, the bite of a banana spider may result in milder effects. Nonetheless, it’s always wise to take precautions and avoid provoking these fascinating arachnids.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do banana spiders change the color of their webs to match their surroundings?
Banana spiders change the color of their webs to match their surroundings through color adaptation and camouflage techniques. This allows them to blend seamlessly into their environment, enhancing their hunting success and evoking awe in their mastery of disguise.
What is the lifespan of a banana spider?
The lifespan of a banana spider is relatively short, living for only a few months. They reproduce once a year and their mating behavior involves the male presenting a gift to the female. Banana spiders use their intricate webs and hunting techniques to catch flying or jumping insects.
How often do banana spiders reproduce?
Banana spiders reproduce once a year, engaging in a complex mating ritual. The female releases pheromones to attract a male, who must carefully approach to avoid being mistaken for prey. They mate, and the female lays eggs in a silk sac, which she guards until they hatch.
Where is the Sydney funnel web spider found?
The Sydney funnel web spider is found in Sydney, Australia. It prefers habitats with high humidity, such as rainforests and wetlands. It is known for its aggressive behavior and strong fangs capable of piercing leather.
What are the symptoms of a bite from the Sydney funnel web spider?
The symptoms of a bite from the Sydney funnel web spider include immediate pain, sweating, muscle spasms, and difficulty breathing. Treatment options for a bite include applying pressure to the wound, immobilizing the affected area, and seeking medical assistance immediately. The venom composition differs between male and female Sydney funnel web spiders, with the male’s venom being more potent.
Key Takeaways About Banana Spiders
– Banana spiders are venomous arachnids with a body length of 1 to 3 inches.
– Female banana spiders are larger than males and have a spotted orange, yellow, or tan abdomen.
– Banana spiders primarily feed on flying or jumping insects and use their keen eyesight and vibration-sensing leg hairs to detect movement and select their prey.
– Banana spiders have less potent venom compared to other venomous spiders like the Sydney funnel web spider, and their bites can cause mild discomfort similar to a bee sting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, banana spiders are fascinating venomous arachnids with unique traits. Their diet mainly consists of flying or jumping insects, which they capture in their large, intricate webs. They prefer warm, humid environments like forests or swamps, but can also be found in urban areas.
While their venom is not dangerous to humans, there have been rare cases of individuals with pre-existing conditions experiencing adverse effects. For example, a study conducted in 2017 documented a hiker who developed a severe allergic reaction after being bitten by a banana spider. Although these instances are rare, it’s important to exercise caution when encountering these intriguing creatures.