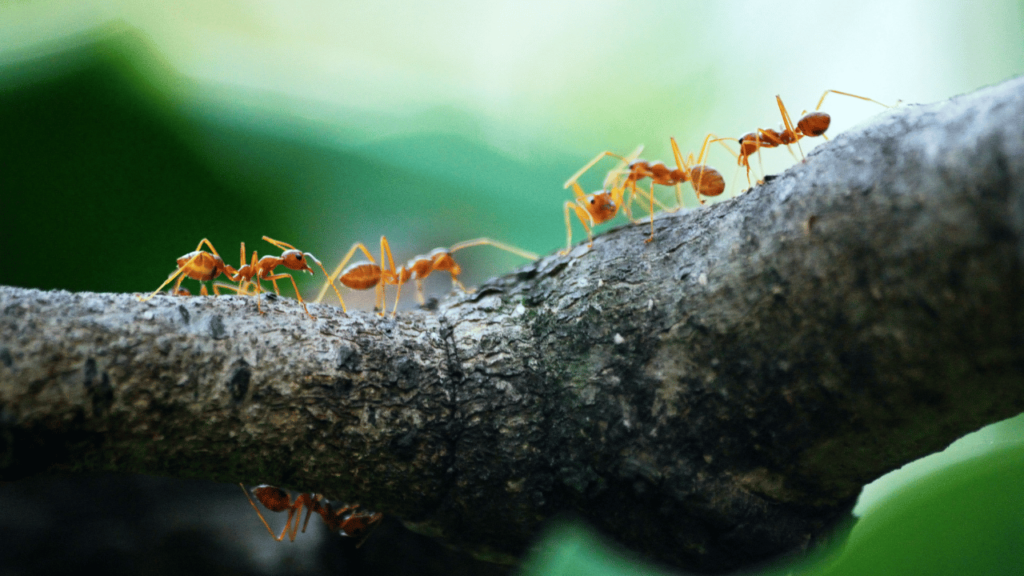
Do ants sleep? Are you ready to dive into the secret world of ant sleep? Prepare to be amazed as we uncover the fascinating patterns of sleep in ant queens and workers. While these tiny creatures may seem insignificant, their sleep habits are anything but. In this article, we will explore the intricate mechanisms of ant sleep, shedding light on the remarkable behaviors of these industrious insects.
Just like humans, ants have their own unique sleep patterns. But don’t expect them to hit the snooze button or curl up in cozy beds. Ants have a different approach to sleep, one that involves napping throughout the day and conserving energy when needed. This idiom of ‘working smarter, not harder’ is embodied by these remarkable creatures.
Queens, the rulers of ant colonies, have their own sleep routine. They indulge in dozing and deep sleep, alternating between these two states throughout the day and night. It’s truly extraordinary how queens can sleep for up to nine hours a day, rejuvenating their bodies and minds for the demands of colony leadership.
On the other hand, worker ants, the backbone of the colony, have a slightly different sleep pattern. They take around 200 one-minute naps per day, allowing them to rest and recharge in short bursts. These hardworking females carry out various tasks, from foraging for food to caring for the larvae, and their strategic napping helps them maintain their tireless work ethic.
Join us on this journey as we unravel the mysteries of ant sleep. Through a scientific lens, we will delve into the sleep mechanisms of queens and workers, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of these captivating sleep patterns. Get ready to expand your knowledge and gain mastery over the intriguing world of ant sleep.
Ant Sleep Mechanism
Do you ever wonder how ants sleep and what mechanisms they use to rest? Sleep deprivation in ants is an intriguing topic that sheds light on the role of sleep in ant colony dynamics.
While ants don’t sleep like humans, they do have periods of rest to conserve energy. Worker ants take over 200 one-minute naps per day, while queen ants sleep in six-minute intervals for up to nine hours per day. This periodic rest is crucial for maintaining the overall functionality of the colony.
Sleep deprivation in ants can have detrimental effects on their cognitive abilities, foraging efficiency, and overall productivity. Therefore, the sleep patterns of both worker and queen ants play a vital role in the coordination and success of the colony.
Understanding these mechanisms can provide valuable insights into the complex social dynamics within ant colonies.
Sleep Patterns of Queens
Get ready to discover the intriguing sleep patterns of queen ants! The sleep patterns of queen ants differ from those of worker ants in terms of duration and frequency. While worker ants take over 200 one-minute naps throughout the day, queen ants sleep in six-minute intervals for up to nine hours per day. This stark contrast in sleep duration is crucial for the queen’s reproductive success and overall behavior. Research has shown that sleep deprivation can significantly impact ant queen behavior, leading to decreased fertility and impaired decision-making abilities.
In comparison to worker ants, queen ants have longer and more consolidated sleep periods, allowing them to recharge and maintain their vital reproductive functions. These differences in sleep patterns highlight the importance of sleep for ant queens and provide valuable insights into their unique biological processes.
| Sleep Patterns | Queen Ants | Worker Ants |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 6 minutes | 1 minute |
| Frequency | 9 hours | 200 naps |
| Importance | Reproduction, decision-making | Energy conservation, rest |
Sleep Patterns of Workers
Explore the intriguing sleep habits of worker ants and the significant impact it has on their daily routines.
Worker ants, being the backbone of the colony, depend on regular bouts of sleep to maintain their productivity. However, sleep deprivation can have a detrimental effect on their efficiency. Studies have shown that when worker ants are sleep-deprived, their foraging and food-gathering abilities decline significantly. This leads to a decrease in the overall productivity of the colony.
When comparing the sleep patterns of worker ants with those of other insect species, it’s evident that ants have a unique sleep schedule. Unlike bees, who sleep for longer durations, worker ants take numerous short naps throughout the day. These one-minute naps allow them to rest and conserve energy without compromising their duties. This adaptation enables worker ants to stay active and responsive to the needs of the colony, ensuring its survival and success.
Understanding the impact of sleep deprivation on worker ants’ productivity and the comparisons with other insect species’ sleep patterns provides valuable insights into the complex world of ant behavior and colony dynamics.
Video by Signatures Science – Hut
Frequently Asked Questions
How do ants communicate with each other during their sleep?
Ants do not communicate with each other during sleep as they enter a state of torpor to conserve energy. Their sleep patterns are different from humans, and they do not have designated sleep cycles.
Can ants dream during their sleep?
Ant sleep research suggests that ants do not dream during their sleep. However, their sleep cycles are fascinating, with worker ants taking over 200 one-minute naps per day and queens sleeping in six-minute intervals for up to nine hours.
Do ants experience sleep disorders or disturbances?
Ants experience different sleep stages, including dozing and deep sleep. Sleep deprivation can have negative effects on ants, impairing their cognitive abilities, foraging efficiency, and overall lifespan.
Are there any differences in the sleep patterns between different ant species?
Comparative analysis reveals that different ant species exhibit variations in sleep patterns. This evolutionary significance plays a crucial role in the functioning of ant colonies, ensuring efficient foraging, nest maintenance, and protection of the queen.
How do external factors, such as temperature or food availability, affect ant sleep patterns?
Temperature and food availability can greatly impact ant sleep patterns. Extreme cold may cause ants to hibernate, while hot weather may reduce their sleep. Additionally, the availability of food can affect the amount of time ants spend resting.
Key Takeaways
– Ants sleep in short intervals throughout the day, with worker ants taking over 200 one-minute naps and queen ants sleeping in six-minute intervals for up to nine hours per day.
– Ants do not have designated sleep chambers and sleep wherever they can find a quiet spot.
– Queen ants have two different sleep states, dozing and deep sleep.
– Ants may hibernate in extreme cold or minimize work during hot weather to conserve energy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sleep patterns of ants, particularly queens and workers, are a fascinating subject of study. Despite their lack of eyelids and unmonitorable brain activity, ants do sleep, with workers taking numerous short naps throughout the day, while queens enjoy longer periods of sleep.
The discovery of two sleep states in queen ants, dozing and deep sleep, adds to the intrigue. It’s remarkable how these tiny creatures, with their diverse tasks and behaviors, find moments of rest and conserve energy. Just like humans, ants also seek out quiet spots to sleep, regardless of the presence of sunlight.
Studying ant sleep patterns can provide valuable insights into the complex lives of these industrious insects. As the saying goes, “Even the tiniest creatures need their rest.”